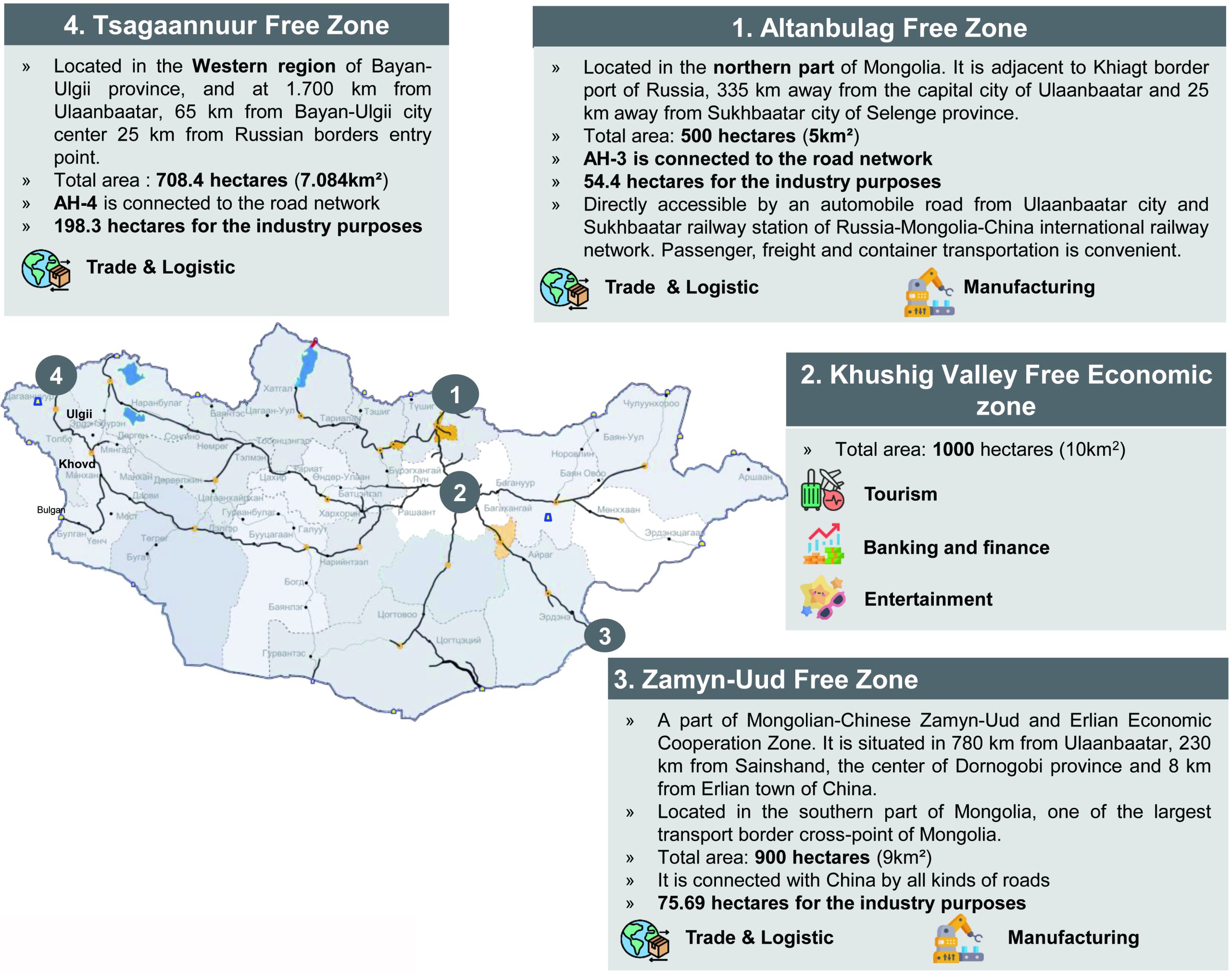
Brief facts
Introduction
Mongolia constantly proves itself to be part of the global market. Mongolia; with discussions to enter bilateral and multilateral agreements, and actively participating in the process of regional integration. To date, Mongolia has established Foreign Investment Protection and Promotion Agreements with 43 countries and Double Taxation treaties with 26. Moreover, Mongolia is a member of the Seoul Convention establishing the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency, and the Washington Convention on the Settlement of Investment Disputes.
In April 2014, Mongolia introduced its investment policy and law to UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) and released the ‘Mongolian Foreign Investment Policy Review’. The overall feedback was positive and accompanied by recommendations and suggestions to the Government of Mongolia. UNCTAD’s main concern was the ‘resource curse’, which prompted the recommendations that were made. Firstly, to avoid macroeconomic instability, the Government of Mongolia had to determine new objectives and tools for a comprehensive foreign direct investment (FDI) strategy. Secondly, the need for new regulatory and institutional reforms; for foreign and local, private sector development. Lastly, Mongolia should develop programs for achieving diversification through FDI, and other activities of foreign companies.
In September 2014, the second review of the trade policies and practices of Mongolia took place and was the basis for a report by WTO Secretariat, and another by the Government of Mongolia. The reviews were similar to UNCTAD`s, which again reinforced the importance of establishing a comprehensive FDI strategy.
In 2015, Mongolia completed the Mongolia-Japan Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) negotiations; the first Foreign Trade Agreement of Mongolia. Like other EPAs, Mongolia-Japan EPA created open doors to both markets; to increase the competitive index of Mongolia and develop the FDI with increases in imports and exports between the two countries. With that, Mongolia made another step to become a bigger player in the global market.


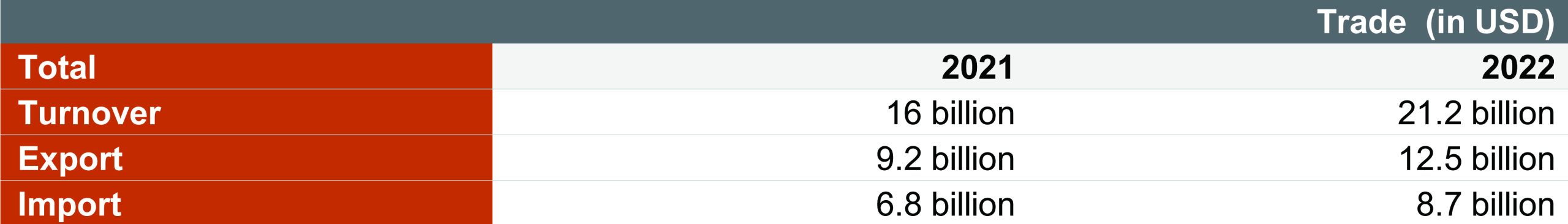 Mongolia’s main export partner is China. In 2022, products exported to China accounted for 84% of the total exports. Other main export partners in the recent years have been Switzerland, Singapore, Republic of Korea and UK.
Mongolia’s main export partner is China. In 2022, products exported to China accounted for 84% of the total exports. Other main export partners in the recent years have been Switzerland, Singapore, Republic of Korea and UK.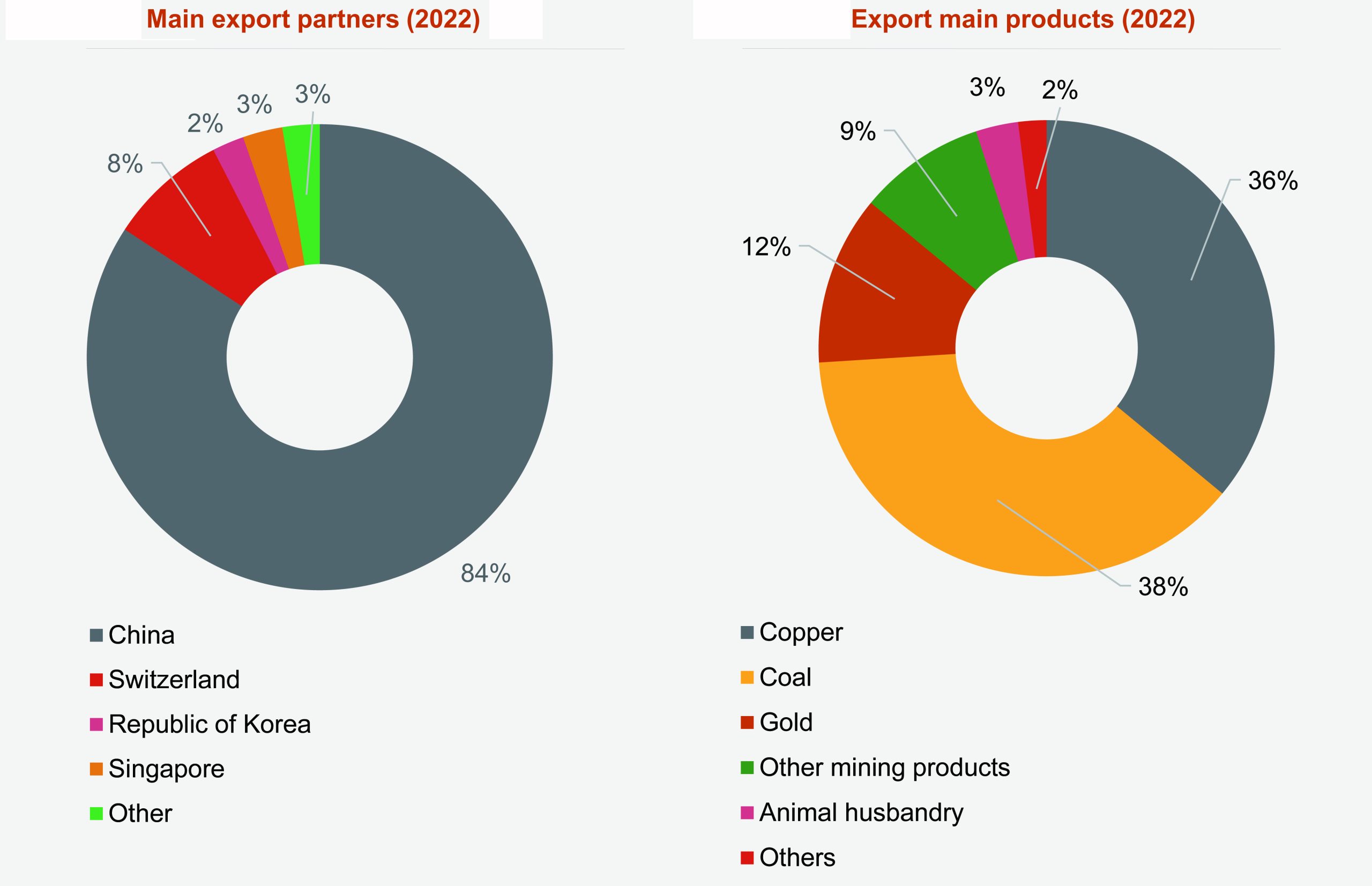
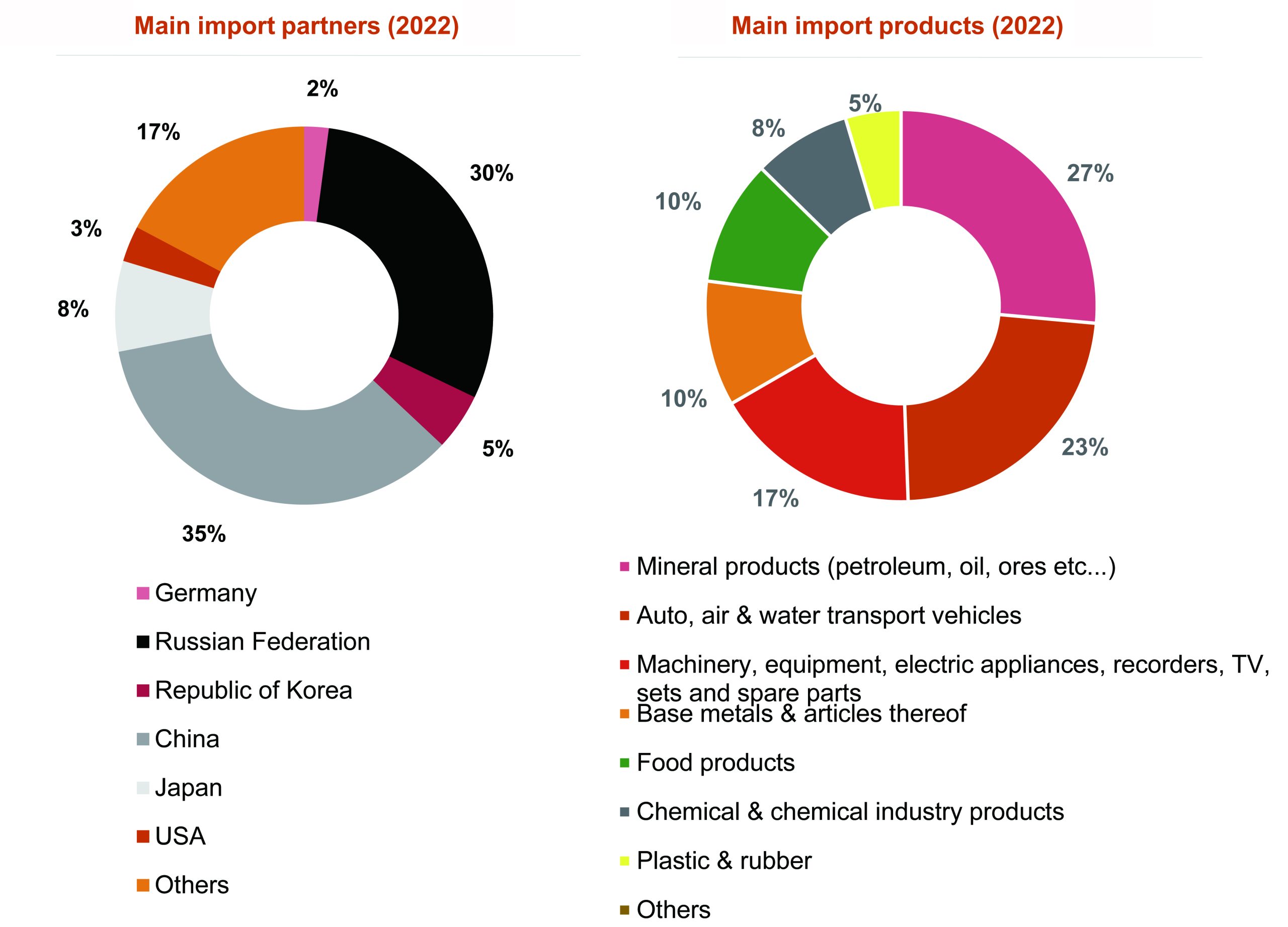
 The European Union’s Generalized Scheme of Preference (EU GSP+)
The European Union’s Generalized Scheme of Preference (EU GSP+)

